Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au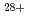 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.